What is HHC? Does this new, hemp-based cannabinoid get you high? Do we even need another hemp-based cannabinoid to get us high (the answer is yes — always yes!). So let’s dive into the details of this new and wonderful compound that is legal across the country — thanks to Congress, of all people! — and answer the question “what is HHC!”
What Is HHC?
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds that are found in the Cannabis sativa plant. There are many cannabinoid variations available, such as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (D9-THC), the primary psychoactive ingredient in cannabis. Other variations include cannabidiol, cannabinol, tetrahydrocannabivarin, etc.
HHC is a cannabinoid compound that has only recently reached the market. Hence, it is sold by a few retailers and primarily as vape carts. Like delta-8 THC, delta-10 THC, and other related cannabinoids, there are many questions about what HHC is, its legal status, where it comes from, and more. So, what is HHC?
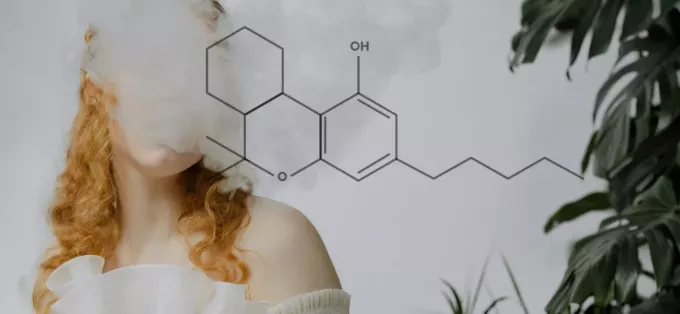
HHC is short for Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol (or simply hexahydrocannabinol). It is a hemp-derived cannabinoid found naturally in cannabis but only in trace concentrations. It is a semi-synthetic hydrogenated compound first created in 1944 by the American chemist Roger Adams when he added hydrogen molecules to delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Hydrogenation modifies the structure of delta 9 THC by replacing a double bond with two hydrogen atoms.
In other words, HHC is the most stable form of THC. It is highly resistant to oxidation, heat, and UV light.
Roger Adams synthesized HHC from conventional cannabis-derived THC. According to Roger Brown, the president and founder of ACS Laboratory: HHC is typically derived from hemp cannabinoids such as delta-8.
What Are The Potential Benefits of HHC?
An old study carried out in 1977 tested HHC on rats. The researchers discovered that the cannabinoid could share properties with narcotic painkillers, but significant differences existed.
A second study carried out in 2007 tested HU211 and HU243 on mice. It found that HHC extended sleeping time by between 80% and 700%. The researchers also wrote that the compound indicated delta-9-THC like effects in the mice, with less powerful therapeutic effects.
Meanwhile, a 2011 research examined a set of HHC analogs, LYR-7 and LYR-8. These compounds can possibly prevent or stop tumor cell growth and angiogenesis, a major stage in the formation of tumors. A study issued in 2010 found that HHC’s manifested for longer periods of time in rats. Generally, aside from the benefits highlighted in the limited studies carried out, there is no proof to support other benefits manufacturers believe HHC has.
Other benefits HHC is believed to have apart from its pain-killing effects include; relief from anxiety, euphoria, relaxation, cerebral and bodily intoxication, reduced inflammation, relief of nausea and vomiting, and better sleep.
How is HHC Produced?
Now that we’ve answered the question “what is hhc,” let’s dive a little deeper. Since HHC is found only in trace amounts in cannabis, extraction from cannabis is not adequate. Hence all HHC available on the market is derived through synthetic procedures in the lab, majorly through THC conversion.
A hydrogenation process carried out in the laboratory produces HHC. This is a similar process used to turn vegetable oil into margarine. It involves the addition of hydrogen atoms to a chemical structure to stabilize it. Typically, THC is saturated with hydrogen in the presence of high pressure and a catalyst like nickel, zinc, or palladium. This breaks THC’s double bond chemical structure and replaces it with hydrogen, forming HHC, yet the cannabinoid’s effects and potency remain essentially unchanged.
Structurally, the difference between delta-8 and delta-9 THC is the position of the bond in the chain of carbon atoms. This means that in delta 8 THC, the double bond is located on the eighth carbon in the carbon chain, while, in delta 9 THC, the double bond is located on the ninth carbon in the carbon chain. The addition of hydrogen during the hydrogenation process replaces the double bond with two hydrogen atoms.
This, in turn, increases the stability of the compound. This is why hexahydrocannabinol is more stable and resistant to thermo-oxidative breakdown compared to tetrahydrocannabinol.
A study from 2007 outlined the possibility of converting CBD into different forms of HHC using gastric juice. However, this experiment was inconclusive.
Is the Production Process Safe?
The scientific director at KCA laboratories in Nicholasville, Kentucky, Richard Sams confirmed that HHC can be produced safely in a well-equipped laboratory, but, if production is scaled up, the risks rise too. “The potential risk here is with explosions”, he explained.
It can be a dangerous process for persons who aren’t qualified or don’t have the right procedures or the right equipment. The catalysts used in production are ‘pyrophoric,’ which means they readily ignite in certain conditions.
What are the Effects of HHC? Does HHC get you High?
Although HHC isn’t technically a THC, the effects of HHC are similar to those of THC. For example, feelings of euphoria, feelings of happiness, increased energy, an elevated body temperature, and heart rate, altered visual and auditory perceptions. Some HHC users describe its effects as more relaxing than stimulating, similar to delta 8.
Every batch of HHC manufactured in the lab is a mix of both active and inactive HHC molecules. A major problem is that manufacturers haven’t figured out a cost-effective way to separate high potency HHC from its low potency twin yet. The active high potency HHC is known as the 9R HHC while the inactive low potency HHC is known as the 9S HHC.
9R HHC actively binds to the body’s natural endocannabinoid receptors, while 9S HHC does not bind as well as 9R HHC because of slight differences in their molecular structures. 9R HHC, the active high potency HHC twin, binds to endocannabinoid receptors to produce effects similar to THC but requires much higher doses of HHC. Richard Sams of KCA Laboratories says, “with a sufficient dose, THC-like effects can be observed.”
Most things known about the effects of HHC are anecdotal. Since HHC and THC are very similar, HHC may offer many of THC’s therapeutic benefits, but not many studies have investigated this. One study on beta-HHC in rats indicated it possesses notable painkilling benefits, but more research is required to assess HHC’s full potential.
In summary, yes, HHC does get you high. And just like THC, the euphoric effect will affect everyone differently. The high lasts about two to three hours depending on some factors. These factors include how much is taken, how the body processes HHC, and how often HHC is used along with other products.
How Potent is HHC?
The psychoactive effects of any type of THC relate to the number of carbons. That means that the longer the carbon chain, the higher the psychoactive potency up to a certain point. According to Greg Gerdeman, Ph.D., cannabis scientist, educator, and the co-founder of NASHCX (Nashville Commodities Exchange), HHC is less potent than delta-9, and potentially more potent than delta-8; however, that varies because the chemistry that creates HHC is not consistent across all methods.
What are the side effects of HHC?
As earlier mentioned, most of the information on HHC is anecdotal and speculative. So far, preliminary research indicates that HHC has a safety profile comparable to THC. That said, users report the same set of side effects common with delta 9 THC users: anxiety and paranoia, dry mouth, dry and red eyes, hunger, and insomnia, rapid heart rate.
Because HHC is synthetic, some persons may even encounter additional undesired side effects. Dr. Ethan Russo, M.D., a board-certified neurologist, and the CEO and founder of CReDO Science says, “The endocannabinoid system is very finely tuned, THC on its own is actually too strong, … so it's called a weak agonist at the CB1 receptor. That means that its affinity for the receptor is low to middling."
“When you have something like the synthetic agonist or like HHC, it’s stronger than that, and it means that you’re very likely to get side effects, maybe even before you get the benefits,” Russo adds.
Does HHC Show Up on A Drug Test?
Another key selling point made by HHC users is that a standard 12-panel drug test won’t detect it. It seems that HHC may not break down in the body in the way THC does. Unlike the delta-8, delta-9, and delta-10 forms of THC, there is some proof that HHC doesn’t metabolize into 11-hydroxy-THC, which is the metabolite that triggers a positive result in many drug panel tests.
James Stephens, vice president of innovation at Creo, a biotech firm specializing in cannabinoids, has seen similar arguments made about HHC not metabolizing into 11-Hydroxy THC. “It could possibly be used to evade drug testing regimes if this proves to be true,” he said.
As of today, no one knows for certain that HHC won’t leave evidence of use in your blood, urine, or hair. If you are to take a drug test soon, we suggest not taking the risk by avoiding HHC.

Is HHC Legal?
The legal status of HHC is controversial and ambiguous. On the report of creators of HHC cannabinoid products such as Bearly Legal, the compound is federally legal because it occurs naturally in the hemp plant. It chose hemp and CBD to produce HHC purposely.
The 2018 Farm Bill federally legalized the hemp plant and all its derivatives, unless the plant or any substance produced from it contains delta 9 THC at a concentration of more than 0.3 percent.
Substantial amounts of CBD are produced from hemp, it also contains many other cannabinoids. Since the Farm Bill legalizes products containing other hemp cannabinoids as long as they don’t exceed the 0.3% THC threshold, producers of HHC products are adamant that everything is above board. The reality is different, however. HHC is conceivably illegal if considered synthetic.
The FDA’s Interim Final Rule (IFR) states that synthetic cannabinoids in hemp are illegal, while naturally-occurring ones are permitted. An argument could be made that HHC occurs naturally in hemp and cannabis but its occurrence is only in trace amounts. HHC manufacturers make it in a lab using a chemical process (hydrogenation) which extracts more of HHC than typically found in hemp.
There is the small matter of the Federal Analog Act, which makes any analog of a Schedule I drug, such as delta-9-THC, a prohibited substance. Therefore, despite the affirmations of HHC manufacturers sellers, the product should be used at the risk of the consumer.
What is the Proper Dose of HHC? How Much Should I Take?
The suitable dose of any psychoactive substance depends on a couple of factors such as weight, age, and tolerance levels.
An individual using HHC for the first time will definitely not know his or her tolerance level but as a general guide, its potency lies somewhere between the mellower high of delta 8 (D8) and the more intense delta 9 THC (D9). All users should always start on the low end. Usually, the delta 8 dosing follows:
-
Low dose: 10 – 20 mg per serving
-
Moderate dose: 20 – 50 mg per serving
-
Heavy dose: 50 – 100 mg per serving.
Experienced users of delta 8 can take an HHC dose equal to the delta 8 doses normally taken, but to be on the safer side, it is recommended to start using a slightly lower dose. If you are completely new to THC and its cannabinoids, then it’s best to take a small amount, or perhaps even a microdose (1–2 mg), before gradually increasing the dose.
A school of thought believes that HHC is 80% as potent as delta-9-THC, individuals with a low THC tolerance should use HHC with caution. They should take no more than 3-5mg at first to gauge its effects on the body and mind
Can You Build Up Tolerance to HHC?
HHC is a cannabinoid and just like THC and other cannabinoids, it is quite normal to build up a tolerance after consistent use. Most times, discontinuing use for a bit resets a user’s tolerance.
Is it Safe to Take HHC?
There is very little research on the long-term use of HHC. Hemp-derived cannabinoids (HHC included) are not under cannabis regulations in legal adult-use states, because of this, HHC manufacturers are not required to test their products for purity and potency.
Generally, the safety of HHC is unknown but, there have been no reports of overdose or death from using HHC or its products.

How Does HHC Compare to Other Cannabinoids?
It has been reported that the effects of HHC are very similar to the effects of Delta 8 THC and Delta 9 THC. HHC is THC, meaning that the two compounds are relatively identical when it comes to their molecular structure. But, HHC lacks double bonds in its structure. That’s because, during the manufacturing process, hydrogenation breaks down and replaces the double bonds already found in THC.
HHC vs Delta 10 THC
HHC is more intoxicating than delta 10 THC, and its psychoactive properties seem to give a feeling of euphoria and inner bliss. This means that HHC products can make a user feel groggier than they would with delta 10, since it can be more turbulent to a person’s normal thought process.
|
HHC |
Delta 10 |
|---|---|
|
Hexahydrocannabinol |
Tetrahydrocannabinol |
|
Double bond absent in its carbon chain |
Double bond present on tenth carbon |
|
More intoxicating |
Less intoxicating |
HHC vs Delta 9 THC
HHC behaves identically to delta 9 THC. Researchers say that it offers the same effects as delta 9 that relate to mood, sleep, nausea, appetite, pain, and more. We know that the effects of delta 9 are extensive throughout the body through its interest in both CB1 receptors (cannabinoid receptors in the nervous system) and CB2 receptors (cannabinoid receptors in the digestive and immune systems). HHC varies from delta 9 due to the absence of the double bond in HHC. The lack of this double bond affects how HHC interacts with endocannabinoid receptors. Thus, this makes hexahydrocannabinol less powerful than delta 9.
|
HHC |
Delta 9 |
|---|---|
|
Hexahydrocannabinol |
Tetrahydrocannabinol |
|
Double bond absent in its carbon chain |
Double bond present on ninth carbon |
|
Less intoxicating |
More intoxicating |
HHC vs Delta 8 THC
Delta-8 THC can create a tenuous high that is relaxing and uplifting just like HHC but less potent. Compared to Delta -8, HHC is more sedative and relaxing.
|
HHC |
Delta 8 |
|---|---|
|
Hexahydrocannabinol |
Tetrahydrocannabinol |
|
Double bond absent in its carbon chain |
Double bond present on eighth carbon |
|
More intoxicating |
Less intoxicating |
HHC vs CBD
CBD stands for cannabidiol. The major difference between cannabidiol and hexahydrocannabinol is that CBD cannot give a user the psychoactive effects that HHC and delta-9 produce. They have similar pharmacological benefits such as elevation of pain, offset of anxiety and depression, and improving sleep.
|
HHC |
CBD |
|---|---|
|
Hexahydrocannabinol |
Cannabidiol |
|
Gives an intoxicating euphoric high |
No psychoactive effects |
Things to Take Away (Final Thoughts on HHC)
-
HHC is short for hexahydrocannabinol and is a more stable, hydrogenated form of THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol).
-
HHC has a longer shelf life than THC.
-
Hexahydrocannabinol is a mix of 9R HHC and 9S HHC (less potent) when produced.
-
Delta-9-THC is more potent than HHC which is more potent than delta-8-THC.
-
HHC may not show up in drug tests but it is unverified.
-
There have been no reports of death from the use of HHC.
-
The legality of semi-synthetic HHC is unclear and controversial.
















